CAM has being used all around the world. CAM generally falls into two main types: subtractive and additive.
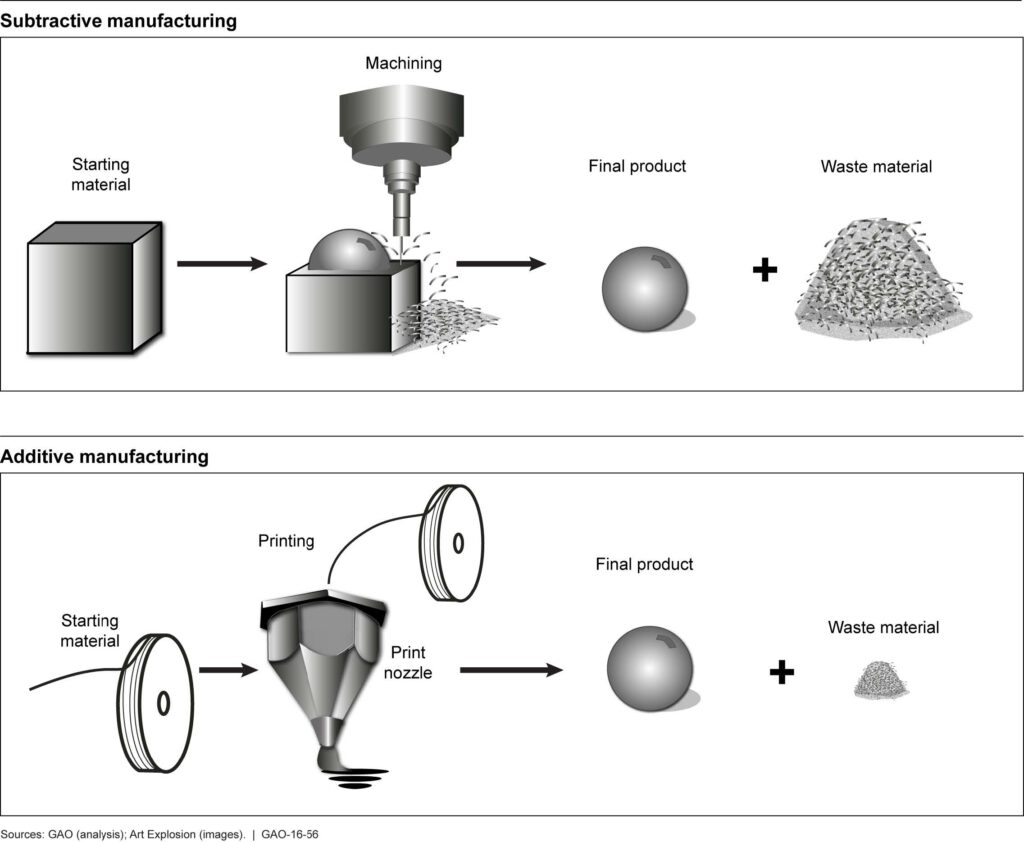
Subtractive processes involve getting rid of material, and this includes the previous example of guiding a cutting tool to cut out a section of cladding. These cutting and shaping processes are currently the more commonly used types of CAM, and the laser cutting of sheet metal is certainly becoming more common. CNC (computer numerical control) machine cutting can be used mostly on workpieces.
Additive processes involve adding material. They are less common at present compare to subtractive according to manufacturing value, but the arrival of 3D printers makes this a very exciting area.

Modular construction is another area where the potential for CAM is huge. In this method, buildings and other structures are assembled from components that are prefabricated offsite in manufacturing plants before being transported to the construction site for assembly. Advances in CAM technology can be used to greatly enhance the efficiency of modular building, and improve the accuracy of the component construction.
One example of modular building is GSK’s ‘factory in a box’. Created using CAD and BIM systems, this provides opportunities that can be shipped to developing areas in crates and put together impressive flat-pack furniture.


